When your burn is the result of negligence, you may be able to recover costs through a personal injury lawsuit
“Burn, baby, burn...” might be the “Disco Inferno” lyrics you love to scream-sing at weddings or 70s nights, but an actual burn is no fun.
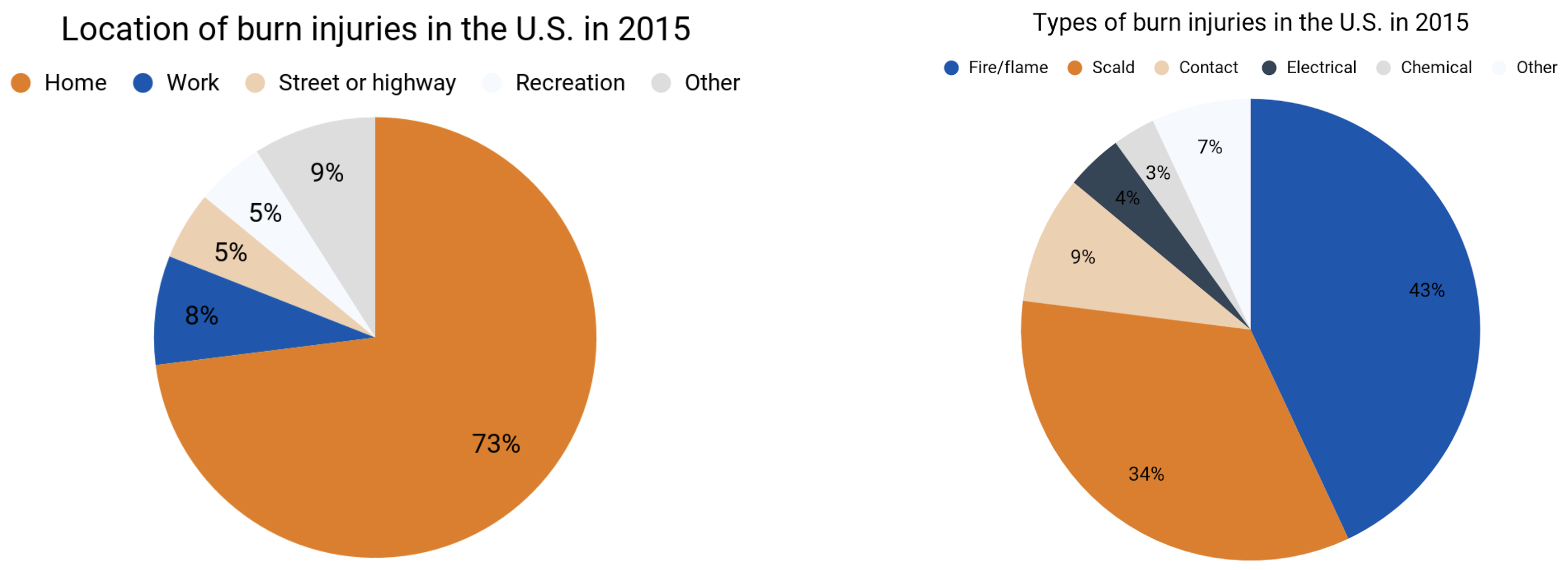
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reports that nearly 500,000 people received burn injury treatment in the U.S. in 2016 at hospitals, clinics, urgent care facilities, and private medical offices. Often, these are minor burns that leave no lasting effects but do require immediate treatment. There were 40,000 burn injuries treated in hospitals, which includes 30,000 admitted to burn centers. Up to 10,000 people die of burn-related infections each year.
Burn injury statistics
Common types of burn injuries
- Scalding, caused when hot liquids come into contact with the skin.
- Electrical burns, which is when the skin is burned by an electrical voltage that can also cause internal damage.
- Chemical burns, when a strong acid or base is in contact with the skin.
- Thermal burns, which are exposure to fire, such as in a car accident, or flammable liquid exposure.
- Gas explosions, caused by a gas leak that catches fire.
- Radiation burns, caused by X-rays, radiation from medical treatment, or tanning beds.
- Inhalation burns from inhaling smoke, steam, or toxic fumes.
Burns are different from deaths related to fire or smoke inhalation.
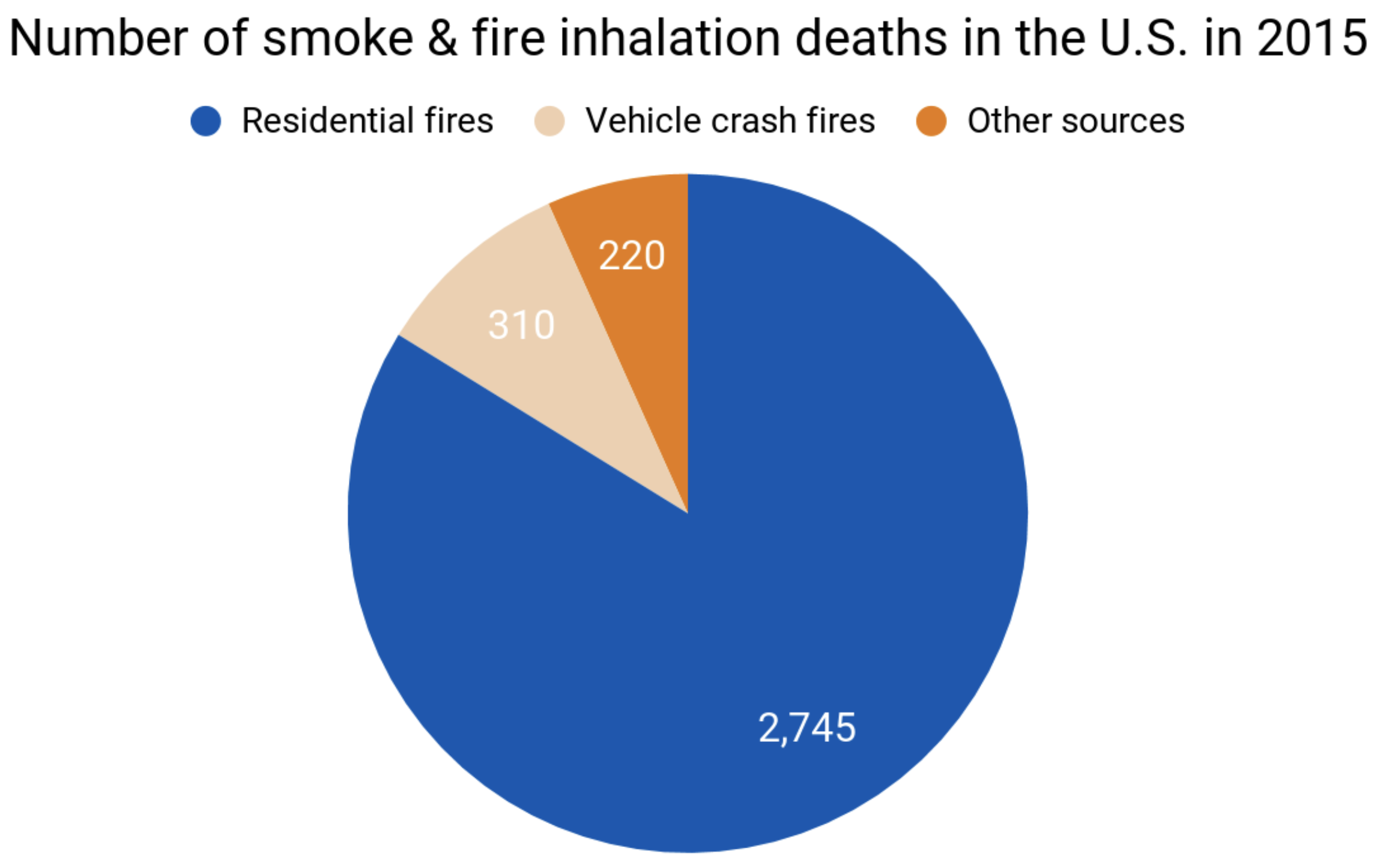
In 2015, there were 3,275 inhalation deaths:
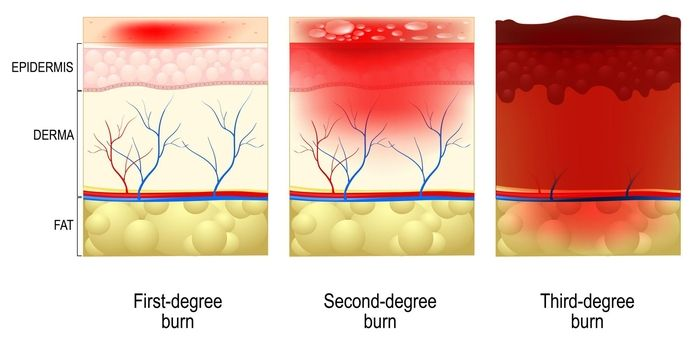
Degrees (types) of burn injuries
Maybe you were burned from taking a pan out of the oven, or accidentally touching a stove burner that was still hot... it could even be a very bad sunburn. These burns often heal on their own after a few days and they’re not the result of anyone’s negligence or wrongdoing (except maybe you could’ve been more careful).
Sometimes, though, we’re burned in a way that doesn’t heal so fast and that requires intensive pain management treatment for a long period of time or other intervention.
All burn injuries are broken into these 3 categories:
- 1st-degree burns. These burns are the mildest and don’t require treatment. They are characterized by some pain, discomfort and reddening of the outer layer of the skin (epidermis). Often, you can use an over-the-counter topical burn remedy available at your local pharmacy or grocery store to soothe the pain and the burn will heal itself in a few days. Sunburn, for example, is a 1st-degree burn.
- 2nd-degree burns. A 2nd-degree burn affects the epidermis and the dermis, or the outer and lower layers of skin. This can include pain, redness, swelling, and blistering.
- 3rd-degree burns. This is the most serious type of burn, and it affects deeper tissues than the skin. It can result in white or black charred skin that could be numb or painful and permanently destroys tissue. A 3rd-degree burn may lead to permanent disfigurement.
Common causes of burn injuries
Many burn injuries are caused by:
- Truck or car accidents
- Workplace injuries
- Defective products
- Electrical accidents
- Scalding water or pipes
- Fires in public places (like restaurants, nightclubs, hotels, etc.)
- Apartment building or home fires
Recovering damages from a burn injury
When you’re injured, you can recover the costs associated with your injury. These include:
- Medical treatment. A personal injury award almost always includes the cost of medical care, both to repay what you’ve already spent on care and to pay for estimated future treatment. Your lawyer will work with experts like doctors, accountants and actuaries to determine what your future medical needs will entail and what they’re likely to cost. Medical treatment costs can include doctor and hospital visits, prescription medication, assistive devices, rehabilitative therapies, and any other costs related to your physical recovery.
- Lost income. You can also claim salary and wages as a loss from an accident. This might include the time you had to take off from work following your injury, a reduction in wages if you had to return to a different job than the one you had before the accident, and loss of earning capacity. Loss of earning capacity is the difference between what you would’ve earned for the remainder of your lifetime and what you will actually earn because of the accident.
- Property loss. If you’re filing a lawsuit because of a car accident, for instance, the cost of replacing or repairing your car would be included under property loss. You’re entitled to the fair market value of any property lost, including your home or other belongings if they were damaged as part of the injury.
- Emotional distress. Emotional distress (pain and suffering) damages compensate a plaintiff for the non-physical effects of an injury. This might include fear, anxiety, sleep disturbances, post-traumatic stress disorder, or other psychological conditions that arise following trauma or serious injury.
- Loss of enjoyment. Anyone who has been injured to the extent that they lose some level of capacity to do the things they previously enjoyed could be eligible for a damage award for loss of enjoyment.
- Loss of consortium. If a loved one has been in an accident and lost the ability to provide love, affection, companionship, comfort, or even the ability to participate in household responsibilities and child-rearing, you might have a loss of consortium claim.
- Punitive damages are a separate award from your other damages. These are intended to punish a defendant or to serve as a deterrent to the defendant from repeating the action or inaction that caused the injury.
Types of burn injury lawsuits
The premise of personal injury law is that it allows legal recovery of damages (expenses) related to medical treatment, lost wages, and other costs. A plaintiff (the injured person) is entitled to be made whole, or restored to the financial condition they’d be in if the injury hadn’t happened, if the injury was caused by another person (or entity) because of negligence.
There are a number of ways that a person or entity (for example, a company or government agency) could be responsible for your injury.
One thing to keep in mind if you’re filing a North Carolina lawsuit is that the state follows a contributory negligence system. That means if you had any portion of fault for your injuries, you can’t recover any damages through a lawsuit.
Most burn injury lawsuits would be one of these types of personal injury lawsuits:
Premises liability lawsuits for burn injuries
If you rent a home or were burned on the premises of any business, you want to know if the landlord or business owner was meeting their obligations for maintaining a safe property.
Premises liability means that as a tenant, your lease guarantees you the right to expect a certain level of safety and security. This includes not just fires, but slip and fall injuries and other situations where you might’ve been hurt by conditions on the property.
Premises liability laws don’t just apply to a rental apartment or house.
The owner of a public place like a restaurant, hotel, stadium, grocery store, gym, public transportation, or other location also has a responsibility to keep patrons safe. That means meeting fire code regulations that include properly marked exits, maintaining capacity, using fire-retardant building materials, and having working sprinkler systems and smoke detectors.
North Carolina Landlord-Tenant Law: Smoke Detectors
A landlord is responsible for filing North Carolina Landlord Forms at the beginning of each tenancy. The forms include a smoke detector notice. North Carolina statute §42-42(a)(5) requires a landlord to:
Provide operable smoke alarms, either battery-operated or electrical, having an Underwriters’ Laboratories, Inc., listing or other equivalent national testing laboratory approval, and install the smoke alarms in accordance with either the standards of the National Fire Protection Association or the minimum protection designated in the manufacturer’s instructions, which the landlord shall retain or provide as proof of compliance.
The requirement is for a tamper-resistant, 10-year lithium battery smoke alarm.
Burn injuries from defective products
North Carolina requires that a plaintiff prove negligence in order to make a successful claim for product liability.
If you were burned while using a consumer product according to the manufacturer’s instructions and in the way it was reasonably intended to be used, you can file a burn injury lawsuit against whichever party (or parties) would be responsible:
- Manufacturer, if it was a manufacturing or design defect.
- Wholesaler or distributor, if the burn was the result of an issue that occurred during the packaging or shipping process.
- Retailer, if it caused the product to become unsafe or should’ve known that that product was unsafe when you purchased it.
Car accident burn injuries
A car accident can cause a burn injury, either because of fire that gets into the car’s passenger compartment or that’s caused by your airbag.
If you receive a burn in a car accident, you would include it as part of your general car accident damages and injuries.
Burn injuries in the workplace
You can sustain a burn injury in any workplace, whether you work in a restaurant, on a construction site, or even in an office.
If that happens, you’d be entitled to receive workers’ compensation benefits.
What to do after a North Carolina burn injury
A burn injury can leave you with serious and lasting effects, and you want to be sure that any future needs are going to be covered.
The first priority after any injury is to get medical treatment. If you feel that a lawsuit is necessary to recover your damages, you need to consult a North Carolina personal injury lawyer. Your lawyer will work with medical and financial experts to determine not only what your current related costs are, but what your costs will be in the future and, if necessary, for the remainder of your lifetime.
See our guide Choosing a personal injury attorney.